eISSN: 2093-8462 http://jesk.or.kr
Open Access, Peer-reviewed

eISSN: 2093-8462 http://jesk.or.kr
Open Access, Peer-reviewed
Jun Won Kim
, Byung Yong Jeong
, Jiyoung Park
10.5143/JESK.2023.42.2.129 Epub 2023 May 05
Abstract
Objective: This study examines the risk factors and improvement measures for infections and musculoskeletal diseases that may occur in food manufacturing workers through a systematic literature review so that food manufacturing workers can work in a safer and healthier environment.
Background: There are previous studies on infections and musculoskeletal diseases of food manufacturers, but systematic studies that summarize and suggest risk factors and improvement measures for infections and musculoskeletal diseases that may occur in food manufacturers are insufficient.
Method: This study was conducted only for research literature among the literature searched using the search formula (("food manufacturing") OR ("food processing") OR ("slaughter") OR ("butchery") OR ("fish industry") OR ("livestock industry")) AND (("musculoskeletal disorders") OR ("infection") OR ("vibration") OR ("awkward posture") OR ("manual heavy loads handling") OR ("repetitive motion") OR ("standing posture") OR ("low temperature")) in the three journal databases of Science Direct, PubMed, and Web of Science.
Results: 725 papers were searched in 3 databases, 3 papers were searched in addition to 3 databases, and 7 out of a total of 728 papers were classified as the categories of infection and musculoskeletal diseases of food manufacturing workers and improvement measures.
Conclusion: In this study, the risk factors of infections and musculoskeletal diseases that may occur in food manufacturing workers were analyzed and each improvement plan was presented to reduce them. The main cause of infection in food manufacturing workers is contact with animals during slaughter, and the incidence of musculoskeletal diseases due to ergonomic factors is high. As such, since food manufacturing workers are threatened by various risk factors, continuous efforts and support are needed to improve the working environment of food manufacturing workers.
Application: This study summarizes the risk factors and improvement measures for infections and musculoskeletal diseases that occur in food manufacturing workers through a systematic literature review, and is thought to be helpful as basic data to create a working environment where food manufacturing workers can work safely and healthily.
Keywords
Systematic review Food manufacturing industry Infection Musculoskeletal disorders Risk factors
한국표준산업분류(Korean Standard Industrial Classification)에 의하면 식료품 제조업은 농업, 임업 및 어업에서 생산된 산출물을 사람이나 동물이 먹을 수 있는 식료품 및 동물용 사료로 가공하는 산업 활동을 말하며 육류, 수산물, 과일 및 채소 가공품, 동물성 및 식물성 유지, 곡물 가공품, 낙농품 및 기타 식료품과 동물용 사료 등을 제조하는 산업 활동으로 구성된다. 또한 식탁용 소금, 화학조미료 및 건강 보조식품 등과 같이 식료품으로 특별히 가공된 제품과 비식용의 육류 분말, 어분 및 동 · 식물성 유지를 가공하는 활동도 포함한다(Statistics Korea, 2017).
세계 식료품 시장 규모는 2020년 기준 전년(4,013.7 십억 달러) 대비 4.25% 증가(4,184.4 십억 달러)하였다(FIS, 2021). 세계 주요 선진 국가들은 자국의 식품 산업을 육성하여 고부가가치와 고용을 창출하고, 국제 경쟁력 확보를 통한 수출 확대를 적극 지원하는 등 식품 산업은 새로운 가치에 주목하고 있으며, 지역별로 유럽의 가공식품 시장의 규모가 가장 크며, 시장의 성장률은 아시아-태평양 지역이 가장 높은 것으로 나타났다(KHIDI, 2010). 식품의약품안전처(Ministry of Food and Drug Safety)에 의하면 2020년 국내 식품 산업 생산실적은 전년(81조 77억 원) 대비 4.1% 증가(84조 3,300여억 원) 하는 등 꾸준한 성장세이며, 생산실적은 국내 총생산(GDP) 대비 4.4%, 국내 제조업 총생산(GDP) 대비 17.6%를 차지하는 것으로 나타났다(MFDS, 2021). 식료품 제조업 시장의 상위 5개 품목을 살펴보면, 부가가치, 사업체 수와 고용 측면에서는 빵과 과자류 제조업이 가장 크고 육류 가공업과 유제품 산업, 음료 분야 및 기타 분야의 규모가 큰 것으로 나타났다. 또한 이들 상위 5개 업종이 전체 매출액의 75%를 차지하고 있으며, 고용과 사업체 수에서는 80% 이상을 차지하는 것으로 나타났다(KREI, 2014).
식품 산업은 국민소득 증가에 따른 소비자의 삶의 질 향상과 소비패턴 변화에 민감하게 반응하며, 수요의 가격과 소득탄력성이 낮아 경기변동에 비탄력적인 특징을 지니고 있다. 또한 소비자의 욕구에 부응하는 다양한 식품을 제공하기 위해서 대량생산체계가 적당하지 않아 대기업보다 중소기업의 비중이 큰 편이다(Han, 2009).
2020년 기준 영국에서 식료품 제조업에 종사하는 근로자는 427,000명으로 나타났으며(Statista, 2022), 미국에서 식료품 가공업에 종사하는 근로자는 139,970명이며, 남성은 89,860명(64.2%), 여성은 50,110명(35.8%)으로 나타났다. 그 중 동물 도살 및 가공업 근로자가 41,025명(29.3%)으로 가장 많은 것으로 나타났으며, 해산물 및 기타 식품업 19,756명(14.1%), 베이커리 및 토틸라 제조업 14,984명(10.7%) 순으로 나타났다(DATA USA, 2022). 국내 식료품 제조업에 종사하는 근로자는 291,529명이며, 남성은 152,549명(52.3%), 여성은 138,980명(47.7%)으로 나타났다(Statistics Korea, 2022).
식료품 제조업 근로자들은 육류, 가금류, 해산물, 생과일, 야채, 곡물, 유제품 등을 가공하며, 곡물, 밀 등의 제품을 제조한다(CollegeGrad, 2022). 따라서 식료품 제조업 근로자는 곡물이나 밀가루의 유기 먼지로 인한 호흡기 질환 발생률이 높으며, 동물과의 접촉으로 인한 브루셀라증, 방선균증 등의 감염, 세척에 사용되는 산, 알칼리, 세제와 같은 자극에 의한 피부염, 반복 작업, 부적절한 자세 등으로 인한 근골격계질환, 냉동 및 냉장 보관에 사용되는 암모니아, 메틸 클로라이드 및 기타 할로겐화 지방족 탄화수소와 같은 냉매로 인한 화학적 화상 등의 위험에 노출된다(ILO, 2011).
질병관리청에 의하면 브루셀라증은 전 세계 어느 곳에서나 발생할 수 있고 전 세계적으로 보고되고 있으며, 브루셀라증은 브루셀라균에 의해 감염된 동물로부터 사람이 감염되어 발생하는 인수공통감염병으로 대개 가축에서 감염되기 때문에 가축을 다루는 직업군에서 발생하는 것으로 나타나고 있다(KDCA, 2020). 살모넬라균 감염 또한 감염된 동물이나 감염된 동물 주변 환경에 접촉으로 인해 발생하기 때문에 가금류, 소와 같은 가축을 다루는 직업군에서 발생하는 것으로 나타났다(KDCA, 2021). 이러한 감염은 전 세계적으로 발생하지만, 공중 보건과 동물 건강 보호 분야에서 개발된 적절한 기준을 가지고 있지 않은 국가에서 가장 널리 퍼져 있는 것으로 나타났다(Galinska and Zagórski, 2013).
식료품 제조업 근로자에게 발생할 수 있는 감염, 근골격계질환에 대한 연구들은 단편적으로 이루어졌으나 이를 종합하여 체계적으로 정리하고 예방 방안을 제시한 연구는 부족한 실정이다. 따라서 본 연구는 체계적 문헌고찰 방법을 활용하여 식료품 제조업에서 도출된 감염 및 근골격계질환과 관련된 문헌을 분석하여 감염 및 근골격계질환의 위험요인을 파악하고 예방 방안을 제시하고자 한다.
2.1 Research strategy
본 연구는 체계적 문헌고찰 보고 지침(PRISMA; Preferred Reporting items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses)을 따른다. 문헌 검색은 한성대학교 학술정보관 국외 학술DB를 통해 2022년 10월 1일부터 2022년 10월 6일까지 실시하였으며, Science Direct, PubMed, Web of Science에서 아래의 검색 식으로 검색된 문헌을 대상으로 연구를 진행하였다.
(("food manufacturing") OR ("food processing") OR ("slaughter") OR ("butchery") OR ("fish industry") OR ("livestock industry")) AND (("musculoskeletal disorders") OR ("infection") OR ("vibration") OR ("awkward posture") OR ("manual heavy loads handling") OR ("repetitive motion") OR ("standing posture") OR ("low temperature"))
2.2 Inclusion criteria
문헌 중 식료품 제조업에서 발생되는 유해 위험요인을 대상으로 한 문헌, 근로자의 감염을 대상으로 한 문헌 그리고 근골격계질환과 관련된 문헌을 포함하였다. 반면, 식료품 제조업이 아닌 연구, 주제가 다른 연구, 체계적 문헌고찰 및 역학 검토 문헌은 배제하였다.
1) 식료품 제조업 근로자의 감염 및 위험요인
2) 식료품 제조업 근로자의 근골격계질환 및 위험요인
3) 식료품 제조업 근로자의 감염 및 근골격계질환 예방 방안
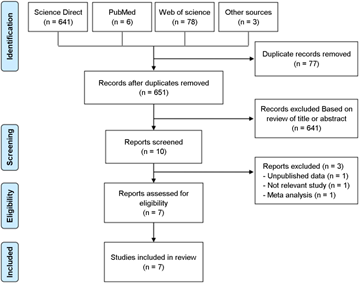
Figure 1은 체계적 문헌고찰을 위한 본 연구의 문헌 선택 진행 상황을 제시하였다. 본 연구에서 사용된 문헌은 Research Article만을 포함하였다. Web of Science 78편, Science Direct 641편, PubMed 6편, 총 725편이며, Science Direct는("food manufacturing" OR "food processing" OR "slaughter" OR "butchery" OR "fish industry" OR "livestock industry")와 "musculoskeletal disorders", "infection", "vibration", "awkward posture", "manual heavy loads handling", "repetitive motion", "standing posture", "low temperature"을 각각 검색하여 총 8회 검색을 진행하였다.
3개의 학술논문 데이터베이스에서 검색된 725편의 문헌은 중 1차적으로 중복된 77편의 문헌을 제외하여 648편의 문헌이 선택되었으며, 문헌 제목과 초록 검토를 통해 연구 목적과 관련이 없는 641편을 제외하였다. 2차적으로 원문이 없는 문헌 1편, 주제와 다른 문헌 1편, 메타 분석 문헌 1편, 총 3편을 제외하였다. 3차적으로 3개의 학술논문 데이터베이스 외 검색된 문헌 3편을 포함하여 최종적으로 7편의 문헌을 가지고 체계적인 문헌고찰을 진행하였다.
3.1 Literature type
Figure 2는 Web of science, Science Direct, PubMed에서 검색한 문헌과 학술논문 데이터베이스 외 검색된 문헌의 종류를 나타낸다. 총 651편의 문헌은 인간 감염 및 근골격계질환 44편(6.8%), 동물 감염 65편(10.0%), 기타 542편(83.3%)로 나타났다.
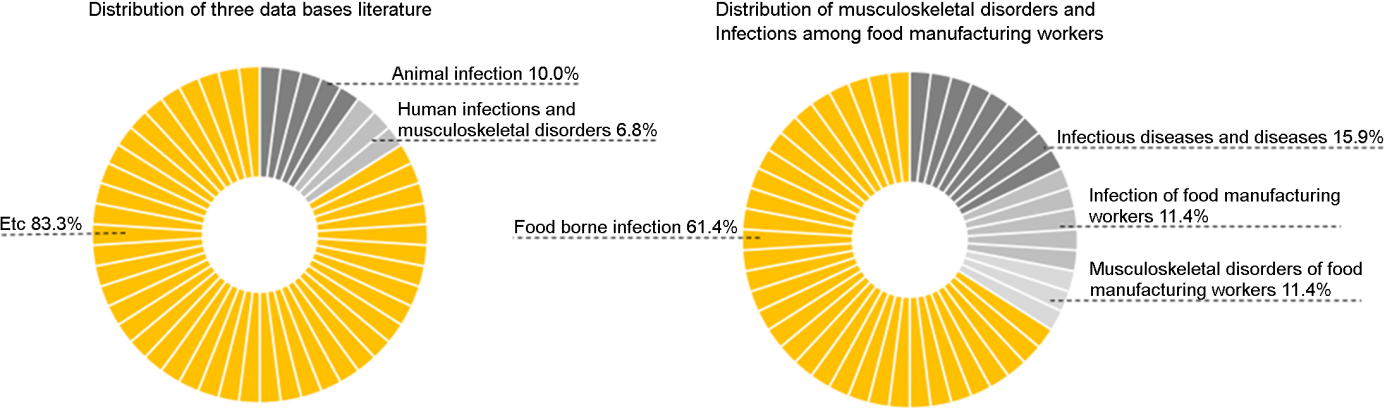
인간 감염 및 근골격계질환에 관한 문헌 44편은 식료품 제조업 근로자와 식료품 제조업 근로자 외 모든 인간에게 발생할 수 있는 감염 및 근골격계질환에 관한 문헌으로 구성되었다. 또한 44편의 문헌은 식료품 제조업 근로자의 감염에 관한 문헌 5편(11.4%), 식료품 제조업 근로자의 근골격계질환에 관한 문헌 5편(11.4%), 식품 매개 감염 27편(61.4%), 전염병 및 질병에 관한 문헌 7편(15.9%)으로 나타났다.
본 연구는 식료품 제조업 근로자의 감염 및 근골격계질환의 위험요인을 분석하고 예방 방안을 제시하는데 목적이 있다. 따라서, 식료품 제조업 근로자의 감염에 관한 문헌 5편, 식료품 제조업 근로자의 근골격계질환에 관한 문헌 5편, 총 10편의 문헌만이 연구 목적에 부합한 것으로 나타났다. 또한 선정된 10편의 문헌 중 연구 목적에 부합하고 원문이 있는 문헌 7편만을 최종적으로 연구 대상으로 선정하였다.
3.2 Literature type by data bases
Table 1은 Web of Science, Science Direct, PubMed에서 검색된 문헌과 학술논문 데이터베이스 외 검색된 문헌의 유형과 분포를 나타낸다. Web of science에서 검색된 문헌은 식료품 제조업 근로자 감염 2편, 식품 매개 감염 10편, 동물 감염 30편, 기타 36편, 총 78편으로 나타났으며, PubMed에서 검색된 문헌은 식품 매개 감염 1편, 동물 감염 2편, 기타 3편, 총 6편으로 나타났다. 또한 Science Direct에서 검색된 문헌 641 중 중복된 문헌 77편을 제외한 564편의 문헌은 식료품 제조업 근로자 근골격계질환 3편, 식료품 제조업 근로자 감염 2편, 식품 매개 감염 16편, 전염병 및 질병 7편, 동물 감염 33편, 기타 503편, 총 564편으로 나타났다. 또한 학술논문 데이터베이스 외 검색된 문헌은 식료품 제조업 근로자 근골격계질환 2편, 식료품 제조업 근로자 감염 1편, 총 3편으로 나타났다.
|
Data bases |
Human infection and musculoskeletal disorders |
Animal |
Other |
||||
|
Musculoskeletal |
Infection of |
Food borne |
Infectious |
||||
|
Web of Science |
N = 78 |
- |
2 |
10 |
- |
30 |
36 |
|
100.0% |
- |
2.6% |
12.8% |
- |
38.5% |
46.2% |
|
|
PubMed |
N
= 6 |
- |
- |
1 |
- |
2 |
3 |
|
100.0% |
- |
- |
16.7% |
- |
33.3% |
50.0% |
|
|
Science Direct |
N = 564 |
3 |
2 |
16 |
7 |
33 |
503 |
|
100.0% |
0.5% |
0.4% |
2.8% |
1.2% |
5.9% |
89.2% |
|
|
Other sources |
N
= 3 |
2 |
1 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
|
100.0% |
66.6% |
33.3% |
- |
- |
- |
- |
|
|
Total |
N
= 651 |
5 |
5 |
27 |
7 |
65 |
542 |
|
100.0% |
0.8% |
0.8% |
4.1% |
1.1% |
10.0% |
83.3% |
|
식품 매개 감염에 관한 문헌으로는 날고기 또는 덜 익힌 고기 섭취로 인한 toxoplasmosis gondii 감염(Deng et al., 2020), 감염된 젖소의 원유 섭취로 인한 mycobacterium bovis 감염(Collins and More, 2022), 미리 포장된 썰어둔 토마토에서의 살모넬라균으로 인한 감염 및 오염된 로메인 상추 섭취로 인한 대장균 감염(Swanger and Rutherford, 2004) 등으로 나타났다.
전염병 및 질병에 관한 문헌으로는 출혈열 바이러스 감염으로 나타나는 급성 발열성 출혈성 질환(VHF)의 인간 간 전염(Leblebicioglu et al., 2016), 탄자니아를 포함한 라틴 아메리카, 아시아 및 사하라 사막 등 저소득 국가에서 널리 퍼진 인수공통전염병 기생충인 Taenia solium (Trevisan et al., 2017) 등으로 나타났다.
동물 감염에 관한 문헌으로는 세계 축산업계에서 가장 악명 높은 병원체 중 하나이며 질병인 구제역(Kangli et al., 2021; Visser et al., 2019), 열악한 수질, 오염된 먹이 및 스트레스 요인으로 인한 물고기의 감염(Hossain and Heo, 2021), 가축 산업에 영향을 미치는 소 근막염(Odeniran et al., 2020), 가축 산업에서 상당한 경제적 손실을 초래하는 브루셀라증(Quintero et al., 2018)에 관한 문헌 등으로 나타났다.
기타 문헌으로는 식품 산업에서 공정 제어를 위한 센서 및 계측 기술의 현재 상태에 관한 연구(Pedersen, 1991), 동물 사료의 항생제 및 합성 성자 촉진제에 관한 연구(Ronquillo and Hernandez, 2017), 동물의 건강 상태를 측정하고 시간 경과에 따라 모니터링 하는 도구 개발에 관한 연구(Depoorter et al., 2015), 구충제 저항성에 관한 연구(Sangster, 1999), 낙농 부문의 미래 탄력성에 대한 농업 환경 계획에 관한 연구(Coyne et al., 2021), 기생충 질병 근절에 관한 프로그램 연구(Bowman, 2006), 반추 동물의 부결핵(Johne's disease)과 관련된 STATD의 수정된 버전을 개발하기 위한 연구(Gardner et al, 2011) 등으로 나타났다.
본 연구는 식료품 제조업 근로자에게 발생하는 감염 및 근골격계질환의 위험요인을 파악하고 예방 방안을 제시하는 데 있다. 따라서, 연구의 목적에 부합하지 않은 식품 매개 감염, 전염병 및 질병, 동물 감염, 기타 문헌은 배제하고 식료품 제조업 근로자의 감염에 관한 문헌 5편(10%), 근골격계질환에 관한 문헌 5편(7%), 총 10편의 문헌 중 연구 목적에 부합하고 원문이 있는 문헌 7편만을 연구 대상으로 선정하였다.
3.3 Risk factors and symptoms of infection
Table 2는 감염에 대하여 연구된 문헌으로 저자(출간 연도), 국가(지역), 연구 목적, 연구 대상, 위험요인, 증상으로 분류하고 요약하였다. 감염과 관련된 연구를 살펴보면 브루셀라증에 대하여 연구되었다.
|
No |
Author (Year) |
Country (Region) |
Research purpose |
Participants |
Risk factor |
Symptoms |
|
1 |
Khalili et al. |
Iran |
To evaluate the seroprevalence of |
75 Kerman |
• Exposed to
fresh |
<Brucellosis> • Intermittent fever • Chill • Weakness • Drenching sweat • Back pain • Joint pain |
|
2 |
Galinska |
Poland |
Diagnosis of brucellosis |
- |
• Damaged skin
of •
Aborted foetus or amniotic fluid while performing gynaecological procedures
in cattle • While
examining and flaying slaughtered animals · Headaches • While
handling manure from • Mucous
membranes (mucosa) • Airways |
<Brucellosis> • Mild flu • Severe
complications on the part of the nervous system, musculoskeletal system and
the heart. • Weakness • Undulant fever • Headaches • Pain
involving muscles and joints • Hot flushes • Testicular
pain in men • Fine red rash • Enlarged
liver and spleen • Stomach ache • Diarrhea • Nausea • Vomiting • Constipation • Lack of appetite |
브루셀라증의 혈청 유병률을 평가하기 위한 Khalili et al. (2012)의 연구에 의하면 브루셀라증은 도축장 근로자에게 발생하는 직업병이며, 감염된 동물과 직접 접촉, 감염된 에어로졸화 입자의 흡입을 통해 발생하는 것으로 나타났다. 또한 브루셀라증 환자는 간헐적 발열, 오한, 나른함, 식은땀, 요통, 관절통을 호소하는 것으로 나타났다.
또한 Galinska and Zagórski (2013)의 연구에서도 브루셀라증은 육류 가공 근로자, 사료 가공 근로자에게 가장 발생률이 높은 것으로 나타났다. 브루셀라증은 도축된 동물을 검사하고 껍질을 벗기는 작업 중 발생할 수 있으며, 소의 감염된 태반과 태아와의 접촉을 통해서도 발생할 수 있는 것으로 나타났다. 또한 감염된 동물의 분뇨 취급을 통해 발생할 수 있는 것으로 나타났으며, 점막과 기도를 통해서도 발생할 수 있다고 하였다. 브루셀라증은 발생 시 가벼운 독감에서부터 신경계, 근골격계, 심장에 심각한 합병증에 이르기까지 다양한 증상을 일으킬 수 있는 것으로 나타났다. 또한 고열, 두통, 근육 및 관절 통증, 안면 홍조, 남성의 고환 통증, 미세한 붉은 발진, 간과 비장 비대, 복통, 설사, 메스꺼움, 구토, 변비, 식욕 부진 등 위장 증상뿐만 아니라 심각한 증상으로는 사망 또는 만성 형태로 발생될 수 있는 것으로 나타났다.
3.4 Risk factors for musculoskeletal disorders and areas of pain
Table 3은 근골격계질환에 대하여 연구된 문헌으로 저자(출간 연도), 국가(지역), 연구 목적, 연구 대상, 위험요인, 통증 부위로 분류하고 요약하였다. 근골격계질환과 관련된 연구를 살펴보면 상지 통증 및 손목 터널 증후군, 하지 통증, 요통 등에 대하여 연구되었다.
No |
Author (Year) |
Country (Region) |
Research
purpose |
Participants |
Risk
factor |
Pain
area |
|
1 |
Vellala et al. |
US (Louisiana) |
To compare the results |
Report of injury |
• Inappropriate • Manual handling • High resistance •
Monotonously |
• Hands • Shoulders • Lower back • Neck • Carpal tunnel |
|
2 |
Musolin |
US |
To determine prevalence |
318 Production |
• Highly repetitive • Awkward postures • Exposed to hand |
• Carpal tunnel |
|
3 |
Syron et al. (2018) |
US (Alaska) |
Workers' Compensation |
Workers in |
• Repetitive • Prolonged periods • Heavy lifting |
• Upper • Carpal tunnel syndrome |
|
4 |
Ilardi (2012) |
Chile |
The purpose of this |
14 workers in |
• High frequency • High amount
of |
• Hand • Wrist • Arm • Elbow |
|
5 |
Thetkathuek |
Thailand |
The purpose of this research was to study factors
affecting |
• 528 factory • 255 office |
• Repetitive • Same work posture • Bend |
• Neck • Shoulder |
|
• Alcohol |
• Lower arm |
|||||
|
• Alcohol • Repetitive • Working duration |
• Elbow |
|||||
|
• Repetitive • Low temperatures |
• Hand & Joint • Wrist |
|||||
|
• Working hours • Working duration |
• Knee • Foot & Ankle |
|||||
|
• Standing on a • Body spin |
• Low back |
|||||
|
• Standing on |
• Hip & thigh |
Vellala et al. (1994)의 연구에 의하면 가금류 가공 근로자들은 부적절한 작업 자세, 수동 작업, 절단 작업 시 높은 저항, 단조롭게 반복되는 동작에 의하여 주로 손, 어깨, 허리, 목 등에 근골격계질환 발생 빈도가 높은 것으로 나타났다. 또한, 가금류 가공 근로자들에게 발생하는 손목 터널 증후군은 반복 작업, 부적절한 자세, 권장 TLV 이상의 손 활동 및 힘으로 인해 발생하는 것으로 나타났다(Musolin et al., 2014).
해산물 가공 산업에 속한 근로자들은 반복 작업, 중량물 취급, 장기간 입식 자세의 노출로 인해 상지 통증을 호소하는 것으로 나타났으며(Syron et al., 2018), 연어 산업 근로자들은 연어를 손질하고 뼈를 제거하는 과정에서 반복적인 움직임, 수공구 사용 시 과도한 힘으로 인해 상지 통증을 호소하는 것으로 나타났다(Ilardi, 2012).
냉동식품 제조 근로자들은 반복 동작, 장시간 같은 자세로 서 있는 자세, 굽히는 자세로 인해 목과 어깨 통증이 발생하는 것으로 나타났으며, 알코올로 인해 팔과 팔꿈치 통증이 발생할 뿐만 아니라 반복 동작과 근속 기간이 팔꿈치 통증에 영향을 미치는 것으로 나타났다. 또한 반복 동작과 저온으로 인해 손과 관절 및 손목에 통증이 발생하는 것으로 나타났으며, 근무시간, 근속 기간이 무릎, 발, 발목 통증에 영향을 미치는 것으로 나타났다. 요통의 위험요인으로는 젖은 바닥에서 서 있는 자세, 몸의 회전으로 나타났으며, 엉덩이와 허벅지 통증의 위험요인은 젖은 바닥에서 서 있는 자세로 나타났다(Thetkathuek et al., 2016).
3.5 Measures to improve infection
Table 4는 식료품 제조업 근로자의 감염에 대하여 연구된 문헌으로 브루셀라증 예방 방안에 대하여 분류하였다.
|
No |
Author (Year) |
Country (Region) |
Industry |
Health |
Prevention measures |
|
1 |
Khalili et al. |
Iran |
Slaughterhouse |
Infection |
The disease can be prevented in the slaughterhouse workers through
the use of personal protective devices. Public health authorities should educate the general public
regarding prevention of the disease with specific emphasis on people working
in slaughterhouses. |
도축장 근로자에게 발생할 수 있는 브루셀라증에 대한 Khalili et al. (2012)의 연구에 의하면 도축장 근로자들은 개인 보호 장비를 사용하여 질병을 예방할 수 있으며, 보건 당국은 도축장에서 일하는 사람들을 특별히 강조하여 질병 예방에 대한 일반 대중 교육을 실시해야 한다고 하였다. 따라서 동물 도축에 참여하는 근로자를 인수공통전염병으로부터 보호하기 위한 효과적인 작업 지침을 개발해야 한다고 하였다.
3.6 Measures to improve musculoskeletal disorders
Table 5는 식료품 제조업 근로자의 근골격계질환에 대하여 연구된 문헌으로 근골격계질환 예방 방안에 대하여 분류하였다.
|
No |
Author (Year) |
Country (Region) |
Industry |
Health |
Prevention measures |
|
1 |
Vellala et al. |
US |
Poultry |
Musculoskeletal |
Automation can be
considered to reduce repetitive motion injuries for certain job categories Ergonomic
interventions, work psychology studies, adequate worker supervision, good
injury surveillance information systems, and assessment of workers'
education and training should be adopted to prevent or minimize occupational
injuries and illnesses. Stressful loads to the
back should be avoided and the workers must first be physically tested for
their capabilities in lifting, carrying, pushing, |
|
2 |
Musolin |
US |
Poultry |
Musculoskeletal |
Designing job tasks so
that they are below the ACGIH TLV Automating or semi-automating
front half deboning and thigh deboning tasks Employing a job
rotation schedule in which employees rotate between jobs that use different
muscle groups and that are below the AL of the ACGIH TLV Instituting a medical
surveillance program for MSDs to monitor employee health and determine the
effectiveness of exposure prevention and medical management strategies |
|
3 |
Syron et al. |
US |
Seafood |
Musculoskeletal |
Adjusting workstations
and standing work surfaces to fit the worker height and the angle of the Arranging work stations
so that any lifting is done in front of workers without twisting. Utilizing mechanical
devices that tilt or invert containers in order to reduce manual removal Performing routine and
preventive maintenance to assure that equipment is working properly. Allowing employees
pauses to rest fatigued muscles, as well as breaks in warmer areas of Designing job rotation
schedules between different tasks to "reduce
exposure to any single risk factor and to allow body parts to either rest
completely, work at slower rates, use less force, or work in more neutral
postures". |
|
4 |
Thetkathuek |
Thailand |
Frozen food manufacturing |
Musculoskeletal |
It is advisable to
arrange resting space and pauses for workers who have worked in low temperatures. Supervisors should
arrange a resting time during the workday and individual workers should
request a resting time to refrain from using physical force on the hand when
it is in pain. Stretching exercise is
also recommended. Moreover, workers should be aware of the causes of
musculoskeletal pain, especially those who have worked for more than 5 years. They must receive
information about physiological and subjective reactions, health aspects,
risk of accidents and protective measures, including clothing. Provided with education
about wearing body protection to prevent adverse impacts on their health. |
가금류 가공 근로자에게 발생할 수 있는 근골격계질환에 대한 Vellala et al. (1994)의 연구에 의하면 근골격계질환을 예방할 수 있는 방법 중 하나는 자동화를 통해 특정 직무 범주에 대하여 반복적인 동작으로 인한 부상을 줄일 수 있다고 하였다. 또한 직업상 부상과 질병을 예방하거나 최소화하기 위해 인체공학적 개입, 작업 심리학 연구, 적절한 작업자 감독, 좋은 부상 감시 정보 시스템 및 작업자의 교육 및 훈련 평가가 채택되어야 하며, 등에 스트레스를 주는 하중을 피하고 작업자는 먼저 들어 올리거나 운반하거나 밀거나 당기는 활동에서 자신의 능력을 신체적으로 테스트해야 한다고 하였다. 이와 같이 작업 환경에 세심한 주의를 기울이면 직원 부상의 부작용을 방지하거나 최소화할 수 있다고 하였다.
또한 근로자들이 손의 활동과 힘에 노출되는 것을 줄이기 위해 1) ACGIH TLV 아래에 있도록 작업 설계, 2) 뼈 제거 작업의 자동화 또는 반자동화, 3) 직원들 간에 서로 다른 근육 그룹을 사용하고 ACHIG TLV의 AL 미만인 작업 간에 순환하는 작업 순환 일정 사용, 4) 직원 건강을 모니터링하고 노출 예방 및 의료 관리 전략의 효과를 결정하기 위해 MSD에 대한 의료 감시 프로그램 시행이라는 네 가지 사항을 권장하였다. 따라서, MSD의 위험 요소를 줄이고 MSD의 예방, 조기 인식 및 의료 관리에 대한 기존 지침을 밀접하게 따르도록 가금류 가공 작업을 설계해야 한다고 하였다(Musolin et al., 2014).
해산물 가공 근로자의 근골격계 손상을 피하기 위해서는 1) 작업자의 키와 수행되는 작업의 각도에 맞게 작업대 및 서 있는 작업 표면을 조정, 2) 비틀림 없이 작업자 앞에서 들어 올릴 수 있도록 작업대를 배치, 3) 제품의 수동 제거를 줄이기 위해 용기를 기울이거나 뒤집는 기계 사용, 4) 장비가 제대로 작동하는지 확인하기 위한 정기적 및 예방적 유지 관리 수행, 5) 직원들이 피로한 근육을 쉬게 하고 따뜻한 곳에서 휴식을 취하도록 허용, 6) 단일 위험 인자에 대한 노출을 줄이고 신체 부위가 완전히 쉬거나, 더 느린 속도로 작업하거나, 힘을 덜 사용하거나, 더 중립적인 자세로 작업하도록 서로 다른 작업 간의 작업 순환 일정을 설계라는 여섯 가지 사항을 권장하였다(Syron et al., 2018).
또한 냉동식품 제조공장 근로자의 근골격계 통증을 유발하는 위험요인을 예방하기 위해서는 1) 저온에서 작업한 근로자를 위해 휴식공간과 휴식시간 마련, 2) 감독관은 근무시간 중 휴식시간을 마련하고 근로자 개인은 휴식시간을 요청해 통증 발생 시 손에 물리력을 가하지 않도록 주의, 3) 스트레칭 운동이 권장 및 5년 이상 근무한 근로자 현황 파악, 4) 근로자에게 생리적 및 주관적 반응, 건강 측면, 사고 위험 및 의류를 포함한 보호 조치에 대한 정보 제공, 5) 근로자들의 건강에 부정적인 영향을 방지하기 위해 신체 보호구에 대한 교육을 제공하여야 한다고 하였다(Thetkathuek et al., 2016).
본 연구는 식료품 제조업 근로자의 감염 및 근골격계질환에 영향을 미치는 위험요인을 체계적 문헌 검토를 통해 연구 분석한 논문이다. 총 725편의 문헌 중 최종적으로 선정된 7편의 문헌을 검토한 결과 감염 관련 문헌 2편, 근골격계질환 관련 문헌 5편으로 나타났으며, 이를 체계적으로 정리하였다.
7편의 문헌은 이란, 폴란드, 미국, 칠레, 태국의 식료품 제조업을 대상으로 진행된 연구이며, 7편에 대한 검토 결과 식료품 제조업의 작업 환경 내 다양한 유해 · 위험요인으로 인하여 근로자들에게 감염과 근골격계질환이 발생하는 것으로 나타났다.
4.1 infections
감염을 주제로 한 문헌에서는 이란과 폴란드 도축업에서 발생되는 감염된 동물과의 직접 접촉, 감염된 에어로졸화 입자의 흡입 등의 노출과 근로자의 브루셀라증 사이의 영향을 다루고 있었다.
감염 관련 최종적으로 선정된 2편의 문헌 중 이란을 대상으로 한 Khalili et al. (2012)의 연구에 의하면 브루셀라증은 도축장 근로자에게 발생하는 직업병이며, 감염된 동물과 직접 접촉, 감염된 에어로졸화 입자의 흡입을 통해 발생하는 것으로 나타났다. 또한 폴란드를 대상으로 한 Galinska and Zagórski (2013)의 연구에 의하면 브루셀라증 발병률이 높은 직업군 중 하나는 육류 가공업자이며, 브루셀라증은 도축된 동물을 검사하고 도살하는 동안 직접 접촉에 의해 감염되거나 감염된 동물의 분뇨를 처리하는 과정에서 분뇨와의 접촉으로 인해 발생하는 것으로 나타났다. 이는 식료품 제조업 근로자에게 발생하는 브루셀라증은 세균에 의해 발생하며, 소나 돼지를 만질 때 감염된다는 결과와 일치하였으며(Spellman and Bieber, 2008), 도축업 근로자에게 전염되는 직업병이라는 결과와 일치하였다(Chomel et al., 1994; Kozukeev et al., 2006; Martinez et al., 2003).
인간에게 발병한 브루셀라증은 1932년 처음으로 인식된 이란의 풍토병이며(Kafil et al., 2014), 이란은 브루셀라증 발병률이 세계에서 4위에 해당한다(Haran et al., 2011; Pappas et al., 2006; Ramin and MacPherson, 2010). 이란의 대부분 지역에서는 인간이 가축과 밀접하게 접촉하기 때문에 인간과 동물 브루셀라증의 연간 발병률은 여전히 높은 것으로 나타났으며, 수의사 및 수의학 단체와 농업 및 육류 가공업 근로자 간의 적절한 협력 부족, 국가적으로 잘 설계된 근절 및 통제 프로그램이 수행되지 않았기 때문에 발병률이 높은 것으로 나타났다(Golshani and Buozari, 2017; Pappas, 2010; Leylabadlo et al., 2015). 폴란드에서의 브루셀라증은 도축장 근로자 및 수의사, 육류 가공 근로자에게 주로 발병하는 것으로 나타났다(Olszok and Kucharz, 1994; Siennicki et al., 1960). 폴란드에서 브루셀라증은 수십 년 동안 가축 질병으로서 주요 수의학적 문제 중 하나였으며, 가장 빈번하고 가장 위험한 인수공통전염병 중 하나로 나타났다(Anusz, 1995).
이에 따라 식료품 제조업 근로자들은 생물학적 요인 즉, 박테리아, 바이러스, 균류 등에 의한 감염된 동물을 취급하고 가공하면서 감염(브루셀라증)에 노출되는 것으로 나타났다. 사람의 경우, 브루셀라증은 가벼운 독감과 같은 증상에서부터 신경계, 근골격계 및 심장 부분의 심각한 합병증까지 다양한 증상을 일으킬 수 있다(Galinska and Zagórski, 2013). 따라서, 이러한 감염을 예방하기 위한 대책으로는 감염 예방에 대한 교육, 개인 보호 장비 사용 등이 있다(Khalili et al., 2012). 식료품 제조업 중 육류, 가금류, 해산물을 취급하는 근로자들은 브루셀라증 외에도 살모넬라증, 기생충 감염 등 발생할 수 있는 다양한 위험요인에 노출되고 있으나, 위험요인과 예방 방안을 제시한 연구는 부족한 실정이다. 따라서 육류, 가금류, 해산물을 가공하는 근로자를 중심으로 생물학적 위험요인에 관한 분석과 예방 방안이 필요할 것으로 판단된다.
4.2 Musculoskeletal disorders
근골격계질환을 주제로 한 문헌에서는 미국, 칠레, 태국의 가금류 가공업, 해산물 가공업에서 발생되는 단조롭게 반복되는 동작, 부적절한 작업 자세, 수동 작업, 중량물 취급, 입식 자세 등의 노출과 근로자의 근골격계질환 사이의 영향을 주로 다루고 있었다.
근골격계질환 관련 최종적으로 선정된 5편의 문헌 중 미국의 가금류 가공 근로자, 해산물 가공 근로자들은 반복 작업, 부적절한 자세 등으로 인해 주로 손, 어깨, 허리, 목 등 상지 통증을 호소하는 것으로 나타났다(Vellala et al., 1994; Musolin et al., 2014; Syron et al., 2018). 또한 칠레 연어 산업 근로자와 태국의 냉동식품 제조 근로자들도 반복 작업과 수동 작업, 부적절한 자세 등으로 인해 목과 어깨 등 상지 통증을 호소하는 것으로 나타났다(Ilardi, 2012; Thetkathuek et al., 2016). 이는 식료품 제조업 근로자는 생산 라인에서 반복적인 작업으로 인해 건초염 및 손목 터널 증후군과 같은 작업 관련성 상지 근골격계질환이 직업성 질병의 약 23%를 차지할 만큼 발병률이 높다는 결과와 일치하였다(HSE, 2022). 또한 가금류 생산 근로자는 지속적인 굽힘이 필요한 반복적인 활동으로 인해 허리, 상지, 하지에 통증이 발생한다는 결과와 일치하였으며(Caieiro et al., 2019), 가금류 산업 근로자는 가금류를 매달고 도축하고 운송하는 등 반복적인 작업으로 인해 손, 손목, 팔 및 어깨에 근골격계질환이 발생한다는 결과와 일치하였다(Harmse et al., 2016).
식품가공 산업에서 여전히 수작업이나 고빈도 수작업이 존재하는 것은 불가피하며(Botti et al., 2015), 이러한 수동 작업은 식품 산업 근로자의 근골격계질환 발생에 상당한 영향을 미친다(Ariyanto, 2021). BLS (2008)에 의하면 식료품 제조업은 모든 산업 중에서 부상 및 질병 발생률이 가장 높은 산업 중 하나이며, 동물 도축업은 모든 식품 제조 산업 중에서 가장 높은 발병률을 나타낸다고 하였다. 또한 Spellman and Bieber (2008)에 의하면 식료품 제조업의 많은 생산 근로자는 반복적이고 육체적으로 힘든 작업이 포함되며, 특히 육류 가공 및 가금류 가공 공장 근로자들은 손, 손목, 및 팔꿈치에 반복적인 작업으로 인한 질환에 취약하다고 하였다.
식료품 제조업 근로자들은 인간공학적 요인 즉, 부적절한 자세, 반복 동작, 중량물 취급 등에 빈번하게 노출되는 것으로 나타났다. 인간공학적 요인은 신체에 부담이나 위험을 즉각적으로 알아차리지 못하기 때문에 발견하기가 가장 어려우며, 장기간 노출될 경우 심각한 장기 질병이 발생할 수 있다(NASP, 2018). 근골격계질환의 발생은 근로자의 신체적 활동에 영향을 미쳐 삶의 질을 떨어지게 할 뿐만 아니라 결근에 의한 노동력 손실, 작업의 질의 저하, 산재보상비용의 증가 등으로 이어져 사회, 경제적인 측면에서 많은 문제를 야기하게 된다(Jeong, 2010). 이러한 근골격계질환을 감소시키기 위한 예방 방안으로는 반복 동작 감소를 위한 자동화 또는 반자동화, 작업자의 교육 및 훈련, 작업장 조정 등이 있다(Vellala et al., 1994; Musolin et al., 2014; Syron et al., 2018). 또한 식료품 제조업 근로자들은 인간공학적 위험요인 외에도 다양한 위험요인에 노출되고 있으나, 물리적 위험요인, 화학적 및 생물학적 위험요인, 근로자의 일반적 특성 등 기타 요인과 근골격계질환과의 관계에 관한 연구는 부족한 실정이다. 따라서, 근골격계질환에 영향을 미칠 수 있는 요인들과의 분석과 예방 방안이 필요한 것으로 판단된다.
본 연구는 식료품 제조업 근로자에게 발생하는 감염 및 근골격계질환의 위험요인을 파악하였으며, 감염 및 근골격계질환을 감소시키기 위한 예방 방안을 파악하였다. 식료품 제조업 근로자에게 발생할 수 있는 브루셀라증은 간헐적 발열, 오한, 나른함, 식은땀, 요통, 관절통을 호소하게 되며, 도축장 근로자에게 흔히 발생하는 직업병 중 하나이다. 브루셀라증은 감염된 동물과 직접 접촉, 감염된 에어로졸화 입자의 흡입을 통해 발생하게 되며, 브루셀라증을 예방하기 위해서는 감염 예방에 대한 교육, 개인 보호 장비 사용 등이 필요하다.
또한 식료품 제조업 근로자에게 발생할 수 있는 근골격계질환으로는 상지 통증, 요통이 있었으며, 손, 어깨, 허리, 목 등에 통증을 호소하는 빈도가 높은 것으로 나타났다. 식료품 제조업 근로자에게 발생하는 근골격계질환은 부적절한 작업 자세, 수동 작업, 중량물 취급, 절단 작업 시 높은 저항, 단조롭게 반복되는 동작, 장기간 입식 자세 등이 있었으며, 이는 인간공학적 위험요인이 식료품 제조업 근로자의 근골격계질환에 상당한 영향을 미친다는 것을 보여준다. 근골격계질환의 발병은 발생하는 중증도가 높기 때문에 근로자의 작업 생산성을 저하시키는데 상당한 영향을 미친다. 이러한 근골격계질환을 예방하기 위해서는 인체공학적 개입, 작업 심리학 연구, 적절한 작업자 감독 배치, 작업자의 교육 및 훈련, 작업의 자동화 또는 반자동화, MSD에 대한 의료 감시 프로그램 등이 필요하다.
본 연구는 식료품 제조업 근로자에게 발생되는 감염 및 근골격계질환의 위험요인에 관한 연구 경향을 파악하였으나, 이것이 식료품 제조업의 모든 위험요인을 나타내는 것은 아니다. 또한 본 연구에서 제시된 요인 외에 근골격계질환에 영향을 미치는 직업 불만족, 단조로운 작업, 제한된 직업 통제, 유전적 원인, 성별, 연령 및 기타 요인 등(National Research Council, 2001; NIOSH, 1997) 다양한 시각의 연구가 필요할 것으로 판단되며, 브루셀라증 외 살모넬라증, 기생충 등의 감염 요인과 예방 방안에 관한 연구가 필요할 것으로 판단된다.
반면, 본 연구는 식료품 제조업 근로자의 감염 및 근골격계질환에 영향을 미치는 요인과 예방 방안을 제시하고 있어 감염 및 근골격계질환에 대한 체계적인 예방과 교육을 위한 기초자료로 의미가 있을 것으로 여겨진다. 또한, 식료품 제조업 근로자는 작업 환경 내 다양한 위험요인에 노출되어 건강에 위협을 받고 있는 것으로 나타나 식료품 제조업 근로자의 근로조건 및 작업 환경 예방을 위한 지속적인 노력과 지원이 필요할 것으로 판단된다.
References
1. Anusz, Z., Zapobieganie i zwalczanie zawodowych chorób odzwierzęcych, 1995. Zapobieganie i zwalczanie zawodowych chorób odzwierzęcych - Prolib Integro (mbp.lublin.pl) (retrieved Apr 11, 2023).
2. Ariyanto, J., Control of the risk of musculoskeletal disorders in the food industry: Systematic review, Annals of the Romanian Society for Cell Biology, 25(1), 4254-4261, 2021. Control of the Risk of Musculoskeletal Disorders in the Food Industry: Systematic Review | Annals of the Romanian Society for Cell Biology (annalsofrscb.ro)
Google Scholar
3. Botti, L., Mora, C. and Regattieri, A., Improving ergonomics in the meat industry: a case study of an ltalian ham processing company, IFAC-PapersOnLine, 48(3), 598-603, 2015. Improving Ergonomics in the Meat Industry: A Case Study of an Italian Ham Processing Company - ScienceDirect
Google Scholar
4. Bowman, D.D., Successful and currently ongoing parasite eradication programs, Veterinary Parasitology, 139(4), 293-307, 2006. Successful and currently ongoing parasite eradication programs - ScienceDirect
Google Scholar
5. Bureau of Labor Statistics, Injuries, Illnesses, and Fatalities in Food Manufacturing, 2008. Injuries, Illnesses, and Fatalities in Food Manufacturing, 2008 (bls.gov) (retrieved Oct 13, 2022).
Google Scholar
6. Caieiro, T.T.M., de Assis, D.B., Mininel, N.A., Rocha, F.L.R. and Hortense, P., Musculoskeletal pain: comparison between administrative and production employees of a poultry farming company, Revista Brasileira de Medicina do Trabalho, 17(1), 30-38, 2019. Musculoskeletal pain: comparison between administrative and production employees of a poultry farming company - PMC (nih.gov)
Google Scholar
7. Chomel, B.B., DeBess, E.E., Mangiamele, D.M., Reilly, K.F., Farver, T.B., Sun, R.K. and Barrett, L.R., Changing trends in the epidemiology of human brucellosis in California from 1973 to 1992: a shift toward foodborne transmission. Journal of Infectious Diseases, 170(5), 1216-1223, 1994. https://doi.org/10.1093/infdis/170.5.1216
Google Scholar
8. CollegeGrad, Nature of the Food Manufacturing Industry, 2022. Food Manufacturing Industry: Career, Outlook and Education Information (collegegrad.com) (retrieved Oct 13, 2022).
9. Collins, Á.B., and More, S.J., Parameter estimates to support future risk assessment of Mycobacterium bovis in raw milk cheese, Microbial Risk Analysis, 21, 100204, 2022. Parameter estimates to support future risk assessment of Mycobacterium bovis in raw milk cheese - ScienceDirect
Google Scholar
10. Coyne, L., Kendall, H., Hansda, R., Reed, M.S. and Williams, D.J.L., Identifying economic and societal drivers of engagement in agri-environmental schemes for English dairy producers, Land Use Policy, 101, 105174, 2021. Identifying economic and societal drivers of engagement in agri-environmental schemes for English dairy producers - ScienceDirect
Google Scholar
11. DATA USA, Food processing workers, all other, 2022. Food processing workers, all other | Data USA (retrieved Oct 13, 2022).
12. Deng, H., Arno, S., Wu, Y., Li, X., Li, J., Liu, M., Marieke, O. and van der Giessen, J.W., Quantitative risk assessment of meat-borne Toxoplasma gondii infection in the mainland of China, Microbial Risk Analysis, 14, 100090, 2020. Quantitative risk assessment of meat-borne Toxoplasma gondii infection in the mainland of China - ScienceDirect
Google Scholar
13. Depoorter, P., Van Huffel, X., Diricks, H., Imberechts, H., Dewulf, J., Berkvens, D. and Uyttendaele, M., Measuring general animal health status: Development of an animal health barometer, Preventive Veterinary Medicine, 118(4), 341-350, 2015. Measuring general animal health status: Development of an animal health barometer - ScienceDirect
Google Scholar
14. Food Information Statistics system, Size of overseas food market, 2021. https://www.atfis.or.kr/home/food/stats/main.do? (retrieved Oct 13, 2022).
15. Galinska, E.M. and Zagórski, J., Brucellosis in humans-etiology, diagnostics, clinical forms, Annals of Agricultural and Environmental Medicine, 20(2), 2013. Brucellosis in humans - etiology, diagnostics, c… — Library of Science (bibliotekanauki.pl)
Google Scholar
16. Gardner, I.A., Nielsen, S.S., Whittington, R.J., Collins, M.T., Bakker, D., Harris, B., Sreevatsan, S., Lombard, J.E., Sweeney, R., Smith, D.R., Gavalchin, J. and Eda, S., Consensus-based reporting standards for diagnostic test accuracy studies for paratuberculosis in ruminants, Preventive Veterinary Medicine, 101(1-2), 18-34, 2011. Consensus-based reporting standards for diagnostic test accuracy studies for paratuberculosis in ruminants - ScienceDirect
Google Scholar
17. Golshani, M. and Buozari, S., A review of brucellosis in Iran: epidemiology, risk factors, diagnosis, control, and prevention. Iranian Biomedical Journal, 21(6), 349, 2017. A Review of Brucellosis in Iran: Epidemiology, Risk Factors, Diagnosis, Control, and Prevention - PMC (nih.gov)
Google Scholar
18. Han, D.B., Challenges of Food System in the Era of Globalization, Food Science and Industry, 42(1), 36-38, 2009. https://doi.org/ 10.23093/FSI.2009.42.1.36
Google Scholar
19. Haran, M., Agarwal, A., Kupfer, Y., Seneviratne, C., Chawla, K. and Tessler, S., Brucellosis presenting as septic shock, Case Reports, bcr1220103586, 2011. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bcr.12.2010.3586
Google Scholar
20. Harmse, J.L., Engelbrecht, J.C. and Bekker, J.L., The impact of physical and ergonomic hazards on poultry abattoir processing workers: a review, International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 13(2), 197, 2016. IJERPH | Free Full-Text | The Impact of Physical and Ergonomic Hazards on Poultry Abattoir Processing Workers: A Review (mdpi.com)
Google Scholar
21. Health and Safety Executive, Food and drink manufacture, 2022. Food and drink manufacturing industries (hse.gov.uk) (retrieved Oct 13, 2022).
22. Hossain, S. and Heo, G.J., Ornamental fish: a potential source of pathogenic and multidrug-resistant motile Aeromonas spp, Letters in Applied Microbiology, 72(1), 2-12, 2021. Ornamental fish: a potential source of pathogenic and multidrug-resistant motile Aeromonas spp. - Hossain - 2021 - Letters in Applied Microbiology - Wiley Online Library
Google Scholar
23. Ilardi, J.S., Relationship between producitivity, quality and musculoskeletal disorder risk among deboning workers in a Chilean salmon industry, Work, 41(1), 5334-5338, 2012. Relationship between productivity, quality and musculoskeletal disorder risk among deboning workers in a Chilean salmon industry - IOS Press
Google Scholar
24. ILO, Encyclopaedia of Occupational Health and Safety Food Industry, 2011. Food Industry (iloencyclopaedia.org) (retrieved Oct 13, 2022).
Google Scholar
25. Jeong, B.Y., Ergonomics' Role for Preventing Musculoskeletal Disorders, Journal of the Ergonomics Society of Korea, 29(4), 393-404, 2010. JESK Journal of the Ergonomics Society of Korea
26. Kafil, H.S., baha Hosseini, S., Sohrabi, M. and Asgharzadeh, M., Brucellosis: presence of zoonosis infection 3,500 years ago in North of Iran, Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Disease, 4, S684-S686, 2014. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2222-1808(14)60707-6
Google Scholar
27. Kangli, L., Congcone, W., Fan, Y., Wejjun, C., Zixiang, Z. and Haixue, Z., Virus-Host Interactions in Foot-and-Mouth Disease Virus Infection, Frontiers in Immunology, 12, 57150, 2021. Prevalence of carpal tunnel syndrome among employees at a poultry processing plant - ScienceDirect
Google Scholar
28. Khalili, M., Sami, M., Aflatoonian, M.R. and Shahabi-Nehad, N., Seroprevalence of brucellosis in slaughterhouse workers in Kerman city, Iran, Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Disease, 2(6), 448-450, 2012. Seroprevalence of brucellosis in slaughterhouse workers in Kerman city, Iran - ScienceDirect
Google Scholar
29. Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency, Infectious Disease Homepage, Brucellosis. 2020. https://npt.kdca.go.kr/npt/biz/npp/ portal/nppSumryMain.do?icdCd=NC0012&icdgrpCd=03&icdSubgrpCd (retrieved Nov 12, 2022).
30. Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency, Infectious Disease Homepage, Salmonella infection. 2021. https://npt.kdca.go.kr/ npt/biz/npp/portal/nppSumryMain.do?icdCd=ND0601&icdgrpCd=04&icdSubgrpCd=ND0006 (retrieved Nov 12, 2022).
31. Korea Health Industry Development Institute, Global Trends in the Food Industry, 2010. https://www.khidi.or.kr/board/ view?menuId=MENU01783&categoryId=&linkId=148784 (retrieved Oct 13, 2022).
32. Korea Rural Economic Institute, World Agriculture, 2014. https://repository.krei.re.kr/handle/2018.oak/20884 (retrieved Oct 13, 2022).
33. Kozukeev, T.B., Ajeilat, S., Maes, E. and Favorov, M., Risk factors for brucellosis--Leylek and Kadamjay districts, Batken Oblast, Kyrgyzstan, January-November, 2003. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep, 55(1), 31-34, 2006. Risk Factors for Brucellosis --- Leylek and Kadamjay Districts, Batken Oblast, Kyrgyzstan, January--November, 2003 (cdc.gov)
Google Scholar
34. Leblebicioglu, H., Ozaras, R., Fletcher, T.E. and Beeching, N.J., Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever in travellers: A systematic review, Travel Medicine and Infectious Disease, 14(2), 73-80, 2016. Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever in travellers: A systematic review - ScienceDirect
Google Scholar
35. Leylabadlo, H.E., Bialvaei, A.Z. and Samadi Kafil, H., Brucellosis in Iran: why not eradicated?. Clinical Infectious Diseases, 61(10), 1629-1630, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/civ646
Google Scholar
36. Martínez, C.M., Jiménez, A.P., Cortés-Blanco, M., Chamizo, E.S., Mohedano, E.M., Plata, C. and Navarro, J.M., Brucellosis outbreak due to unpasteurized raw goat cheese in Andalucia (Spain), January-March 2002. Eurosurveillance, 8(7), 164-168, 2003. Eurosurveillance | Brucellosis outbreak due to unpasteurized raw goat cheese in Andalucia (Spain), January - March 2002
Google Scholar
37. Ministry of Food and Drug Safety, Food industry production performance increased 4.1% year-on-year in 2020, 2021. https:// impfood.mfds.go.kr/CFBBB02F02/getCntntsDetail?cntntsSn=407835 (retrieved Oct 13, 2022).
38. Musolin, K., Ramsey, J.G., Wassell, J.T. and Hard, D.L., Prevalence of carpal tunnel syndrome among employees at a poultry processing plant, Applied Ergonomics, 45(6), 1377-1383, 2014. Prevalence of carpal tunnel syndrome among employees at a poultry processing plant - ScienceDirect
Google Scholar
39. National Association of Safety Professionals, Types of Hazards, 2018. https://naspweb.com/blog/types-of-hazards/ (retrieved Oct 13, 2022).
40. National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, Musculoskeletal Disorders and Workplace Factors - A Critical Review of Epidemiologic Evidence for Work-Related Musculoskeletal Disorders of the Neck, Upper Extremity, and Low Back, 1997. Musculoskeletal Disorders and Workplace Factors (97-141) | NIOSH | CDC (retrieved Oct 13, 2022).
Google Scholar
41. National Research Council, Musculoskeletal disorders and the workplace: low back and upper extremities, 2001. Musculoskeletal Disorders and the Workplace: Low Back and Upper Extremities |The National Academies Press (retrieved Oct 13, 2022).
42. Odeniran, P.O., Omolabi, K.F. and Ademola, I.O., Economics model of bovine fasciolosis in Nigeria: an update, Tropical Animal Health and Production, 52(6), 3359-3363, 2020. Economic model of bovine fasciolosis in Nigeria: an update | SpringerLink
Google Scholar
43. Olszok, I. and Kucharz, E.J., Clinical and therapeutic aspects of brucellosis. Przeglad Lekarski, 51(4), 189-192, 1994. [Clinical and therapeutic aspects of brucellosis] - Abstract - Europe PMC
Google Scholar
44. Pappas, G., Papadimitriou, P., Akritidis, N., Christou, L. and Tsianos, E.V., The new global map of human brucellosis. The Lancet Infectious Diseases, 6(2), 91-99, 2006. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(06)70382-6
Google Scholar
45. Pappas, G., The changing Brucella ecology: novel reservoirs, new threats. International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents, 36, S8-S11, 2010. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2010.06.013
Google Scholar
46. Pedersen, L.D., Assessment of sensors used in the food industry, Food Control, 2(2), 87-98, 1991. Assessment of sensors used in the food industry - ScienceDirect
Google Scholar
47. Quintero, A.F., Herrera, D.F.D., Alfonso, D.M., Santana, Y.C., Torres, R.B. and Tamayo, L.M., Evaluation of two rapid immunochromatographic tests for diagnosis of brucellosis infection in cattle, Open Veterinary Journal, 8(3), 236-242, 2018. Evaluation of two rapid immunochromatographic tests for diagnosis of brucellosis infection in cattle | Open Veterinary Journal (ajol.info)
Google Scholar
48. Ramin, B. and MacPherson, P., Human brucellosis. Bmj, 341, 2010. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.c4545
Google Scholar
49. Ronquillo, M.G. and Hernandez, J.C.A., Antibiotic and synthetic growth promoters in animal diets: Review of impact and analytical methods, Food Control, 72, 255-267, 2017. Antibiotic and synthetic growth promoters in animal diets: Review of impact and analytical methods - ScienceDirect
Google Scholar
50. Sangster, N.C., Anthelmintic resistance: past, present and future, International Journal for Parasitology, 29(1), 115-124, 1999. Anthelmintic resistance: past, present and future - ScienceDirect
Google Scholar
51. Siennicki, W., Przylecki, S., Basz, I., Cygankiewicz, M., Pióro, J. and Radziszewska, D., Brucellosisin dairy and meat workers in Poland. Medycyna Weterynaryjna, 16, 267, 1960. Brucellosisin dairy and meat workers in Poland. (cabdirect.org)
Google Scholar
52. Spellman, F.R. and Bieber, R.M., Occupational Safety and Health Simplified for the Food Manufacturing Industry, Government Institutes. 2008. https://play.google.com/store/books/details?id=0rpJExiAZVsC&rdid=book-0rpJExiAZVsC&rdot=1&source= gbs_vpt_read&pcampaignid=books_booksearch_viewport (retrieved Oct 13, 2022).
53. Statista, Number of employees in food manufacturing in the United Kingdom (UK) from 2003 to 2020, 2022. Food manufacturing workforce UK 2003-2020 | Statista (retrieved Oct 13, 2022).
54. Statistics Korea, Current status of business status, 2022. https://kosis.kr/statHtml/statHtml.do?orgId=118&tblId=DT_118N_SAUPN72 &vw_cd=MT_ZTITLE&list_id=118_ATITLE_9_100&scrId=&seqNo=&lang_mode=ko&obj_var_id=&itm_id=&conn_path=MT_ZTITLE&path=%252FstatisticsList%252FstatisticsListIndex.do (retrieved Nov 12, 2022).
55. Statistics Korea, Korean standard industrial classification (KSIC). 2017. http://kssc.kostat.go.kr/ksscNew_web/ekssc/main/main.do# (retrieved Oct 13, 2022).
56. Swanger, N. and Rutherford, D.G., Foodborne illness: the risk environment for chain restaurants in the United States, International Journal of Hospitality Management, 23(1), 71-85, 2004. Foodborne illness: the risk environment for chain restaurants in the United States - ScienceDirect
Google Scholar
57. Syron, L.N., Lucas, D.L., Bovbjerg, V.E., Case, S. and Kincl, L., Occupational traumatic injuries among offshore seafood processors in Alaska, 2010-2015. Journal of Safety Research, 66, 169-178, 2018. Occupational traumatic injuries among offshore seafood processors in Alaska, 2010-2015 - ScienceDirect
Google Scholar
58. Thetkathuek, A., Meepradit, P. and Jaidee, W., Factors affecting the musculoskeletal disorders of workers in the frozen food manufacturing factories in Thailand, International Journal of Occupational Safety and Ergonomics, 22(1), 49-56, 2016. Factors affecting the musculoskeletal disorders of workers in the frozen food manufacturing factories in Thailand: International Journal of Occupational Safety and Ergonomics: Vol 22, No 1 (tandfonline.com)
Google Scholar
59. Trevisan, C., Devleesschauwer, B., Schmidt, V., Winkler, A.S., Harrison, W. and Johansen, M.V., The societal cost of Taenia solium cysticercosis in Tanzania, Acta tropica, 165, 141-154, 2017. The societal cost of Taenia solium cysticercosis in Tanzania - ScienceDirect
Google Scholar
60. Vellala, C., Pine, J.C., Marx, B.D., Farr, A.J., Sistler, F.E. and Aghazadeh, F., Characteristics and cost analysis of injuries & illnesses in poultry processing operations in Louisiana, Journal of Applied Poultry Research, 3(4), 342-354, 1994. Characteristics and Cost Analysis of Injuries & Illnesses in Poultry Processing Operations in Louisiana - ScienceDirect
Google Scholar
61. Visser, L.J., Medina, G.N., Rabouw, H.H., de Groot, R.J., Langereis, M.A., de Los Santos, T. and van Kuppeveld, F.J., Food-and-mouth disease virus leader protease cleaves G3BP1 and G3BP2 and inhibits stress granule formation, Journal of Virology, 93(2), e00922-18, 2019. Foot-and-Mouth Disease Virus Leader Protease Cleaves G3BP1 and G3BP2 and Inhibits Stress Granule Formation | Journal of Virology (asm.org)
Google Scholar
PIDS App ServiceClick here!