eISSN: 2093-8462 http://jesk.or.kr
Open Access, Peer-reviewed

eISSN: 2093-8462 http://jesk.or.kr
Open Access, Peer-reviewed
Taekyung Kim
, Younghwan Pan
10.5143/JESK.2024.43.5.415 Epub 2024 November 04
Abstract
Objective: The purpose of this study is to systematically present the management plan of humanoid robots as urban public facilities through guidelines. In addition, by comprehensively reviewing the placement and operation of robots, maintenance, data security, interaction with users, legal and ethical considerations, etc., a detailed step-by-step implementation plan for management and operation that can optimize the use of robots in public environments is proposed.
Background: The recent public environment is constantly changing with the development of technology, and innovative technologies are actively introduced, especially in areas related to public services. In addition, in some environments, new ways in which robots provide public services are emerging, meaning that robots are increasingly likely to play a role as urban utilities beyond just mechanical tools.
Method: First, a basic guideline system for the efficient operation and management of humanoid robots was established, and second, detailed criteria were derived by specifying the established guidelines. Third, an expert survey was conducted on the system and details of the guidelines to verify their validity. Finally, a detailed implementation plan for each step of the guidelines was derived.
Results: As a result, a detailed implementation plan was proposed step by step to manage humanoid robots as urban public facilities, which is an essential part to ensure the efficient and safe operation of robots. Clear planning and implementation at each stage helps robots prevent various problems that may arise in the process of providing public services in advance and respond quickly when problems arise. In addition, systematic management measures play an important role in continuously optimizing the robot's performance, maintaining the user's trust, and ensuring the long-term operation and stability of the robot as a public facility.
Conclusion: The guidelines presented in this study are significant in that they lay an important foundation for the introduction and operation of humanoid robots as public facilities and provide effective tools for improving the quality of public services and establishing an efficient management system. In future studies, it is necessary to apply the proposed guidelines to the actual operation site, verify the effectiveness of management and operation, and continuously update the guidelines.
Application: This study presents a new concept of public design direction in the future, and can serve as a standard for evaluation and advice in various projects in the public environment in the future.
Keywords
Humanoid robot Public facilities Management Maintenance Guideline Public design
최근의 공공환경은 기술 발전과 함께 지속적으로 변화하고 있으며, 특히 공공서비스와 관련된 영역에서는 혁신적인 기술이 적극적으로 도입되고 있다. 또한 일부 환경에서는 로봇이 공공서비스를 제공하는 새로운 방식이 등장하고 있으며(Shin et al., 2008) 이는 로봇이 단순한 기계적 도구를 넘어 도시 공공시설물로서의 역할을 수행할 가능성이 점점 높아지고 있음을 의미한다.
휴머노이드 로봇(Humanoid Robot)은 인간과 유사한 외형과 동작을 통해 인간과 자연스럽게 상호작용할 수 있는 능력을 갖추고 있는 대상으로(Kim and Pan, 2024), 이 유형의 로봇은 도시 환경에서 다양한 형태의 공공서비스를 제공하는 측면에서 유리한 특징이 있으며, 이를 통해 공공시설물이 수행하는 기능을 대체하거나 보완할 수 있는 잠재력을 지니고 있다. 이러한 관점에서 도시 공공시설물로서 휴머노이드 로봇의 도입은 기술적 혁신 뿐만 아니라 도시 환경의 관리 및 운영 방식에 대한 새로운 패러다임을 제시할 수 있다.
그러나, 도시 공공시설물로서 휴머노이드 로봇을 효과적으로 관리하고 운영하기 위해서는 체계적인 관리 방안이 필수적으로 수반되어야 한다. 이는 사용자와의 상호작용을 고려한 설계를 비롯하여 로봇의 기능적 효율성과 물리적 안정성을 유지하기 위한 관리 체계 및 유지보수 계획을 필요로 하며, 이를 통해 로봇이 공공환경에서 안전하고 책임감 있게 운영될 수 있도록 사전에 고려되어야 한다.
따라서 본 연구의 목적은 도시 공공시설물로서의 휴머노이드 로봇의 관리 방안을 가이드라인을 통해 체계적으로 제시하는 것이다. 이를 위해 먼저 휴머노이드 로봇의 도입이 도시 공공시설물 관리에 미치는 영향을 분석하고, 효율적이고 안전한 운영을 위한 관리조건을 도출하는 것을 목표로 한다. 또한 로봇의 배치 및 운용, 유지보수, 데이터 보안, 사용자와의 상호작용, 법적 및 윤리적 고려 사항 등을 종합적으로 검토하여, 공공환경에서의 로봇 활용을 최적화 할 수 있는 관리 및 운영을 위한 단계별 세부 추진방안을 제안하며, 이를 통해, 휴머노이드 로봇이 도시 공공서비스의 질을 향상시키고, 공공시설물 관리의 새로운 기준을 제시할 수 있는 가능성을 탐색하고자 한다.
2.1 Current status and problems of public facilities
공공시설물(public facilities)은 현대 도시 환경에서 시민들의 생활 편의를 도모하고 사회적 기능을 원활히 수행하기 위해 필수적으로 제공되는 구조물이나 설비를 의미한다(Zhang, 2012). 이러한 시설물은 공공의 이익을 위해 일상적으로 이용할 수 있도록 정부나 공공기관이 설치하고 관리하는 대상으로서, 공공서비스를 위한 다양한 기능과 형태를 갖추는 것이 특징이다. Table 1은 경기도 공공디자인 가이드라인에서 정의하고 있는 공공디자인의 영역과 범위에 대한 분류 체계이다(Design Gyeonggi, 2010) (Design Gyeonggi, 2010) (Design Gyeonggi, 2020) (Design Gyeonggi, 2020).
|
Primary |
Secondary |
Third |
Detailed item |
|
Public space |
Public space |
Parks and |
Park, Pocket park, Waterfront park, Square, Fountain square, Ecological
garden, Arboretum, Forest lodge, Zoo, Botanical garden, Theme park |
|
Street |
Road, Sidewalks, Walking trails, Bicycle path, School zone,
Transportation island, Median, Retaining wall, Cut-out surface |
||
|
Public |
Public office |
Public information center, Village center, Police substation, Fire
station, Post office, Telephone office, Community center, Prison, Government house,
Official residence, Training facilities, Diplomatic office |
|
|
Cultural |
Public gym, Stadium, Concert hall, Civic center, Memorial hall,
Museum, Art exhibition hall |
||
|
Transportation |
Bus terminal, Taxi stand, Train station, Subway station, |
||
|
Environmental |
Public restroom, Drainage facility, Water and sewerage facilities,
Garbage dump, Food treatment facilities |
||
|
Educational |
Kindergarten, School, Research institute, Library, Educational center,
Training center |
||
|
Public facilities |
Urban |
Bridge, Overpass, Pedestrian overpass, Tunnel, Underground |
|
|
Street facilities |
Transportation |
Streetlight, Fence, Bollard, Bus sign, Bicycle locker, Traffic light, |
|
|
Convenience |
Bench, Recycle bin, Drinking fountain, Street stand, Kiosk, |
||
|
Supply facilities |
Manhole, Distribution box, Air vent, Hydrant, Fireplug, Snow removal
box, Thermometer, Hygrometer |
||
|
Public media |
Information |
Milestone, Traffic sign, Bus route map, Tourist map, Subway map, Regulatory
sign, Pictogram, Billboard, Poster, Banner, Signboard |
|
|
Public art |
Sculpture, Mural, Super graphic, Media art,
Graffiti |
||
그러나 공공시설물은 시간이 지나면서 노후화 과정을 거치는 데, 설치환경의 여건상 이를 관리하고 유지하는데 있어 다양한 문제에 노출되어 있으며 특히 시설물은 다양한 관리 주체에 의해 분산적으로 관리되기 때문에 일관된 유지보수 시스템 부족으로 인한 관리의 비효율성이 주요 문제로 자주 지적되고 있다(Choi et al., 2020). 그리고 기후 변화, 자연재해, 환경 오염 등 외부 요인에 의해 쉽게 손상될 가능성 또한 높지만, 이러한 요소에 대비한 적절한 보호 대책이나 보수 계획이 부족한 경우가 많다.
이렇듯 다양한 공공환경에 배치되고 운용중인 공공시설물은 관리 및 유지보수 관점에서 여러 가지 문제점이 지속적으로 발생하고 있으며, 이러한 문제점들은 공공시설물의 장기적이고 효율적인 운영을 저해하고, 공공서비스의 질적 저하를 초래하는 원인이 되고 있다(Park et al., 2011).
2.2 Transition of public facilities to humanoid robot concepts
공공시설물을 휴머노이드 로봇으로 대체하는 것은 공공환경 관리 측면에서 운용 및 관리에 대한 유연성과 실시간 대응능력을 높이고, 공공자원의 효율성을 크게 향상시키는 중요한 의미를 갖는다.
첫째, 로봇은 사용자와 자연스럽게 상호작용 하는 것을 전제로 다양한 공공시설물의 기능을 통합하고 업데이트 할 수 있어, 유지보수 비용과 시간을 절감할 수 있으며, 실시간 모니터링과 자동화된 관리로 공공시설의 효율적 운영을 가능하게 하는 장점을 갖고 있다. 이는 실시간으로 변화하는 공공환경의 상황에 효과적으로 대응할 수 있으며, 로봇이 각종 환경에서 공공서비스의 질을 향상시키는데 중요한 역할을 수행할 수 있다.
둘째, 기존의 시설물의 구조적 한계로 업그레이드가 어려웠던 일부 공공서비스의 업그레이드를 고려할 수 있는 계기가 될 수 있다. 예를 들어 로봇이 제공하는 공공서비스는 사용자에게 적극적으로 다가가는 능동적인 차원의 서비스가 가능해 진다(Chung, 2020). 이는 다양한 사용자에게 좀더 쉽게 사용이 가능한 새로운 방식의 공공서비스를 제공하는 것에 대한 새로운 계기가 될 수 있다.
셋째, 로봇의 통합된 관리를 전제로 좀더 효율적인 관리 체계가 가능해진다. 이는 새로운 공공서비스 환경을 발굴하고 개척하는 계기로 작용할 수 있다. 기존의 시설물로는 충분한 서비스가 어려웠거나 환경조건의 제약으로 인해 서비스의 확장이 불가능했던 환경이나 공간을 새롭게 발굴하고, 이를 새로운 로봇 서비스 영역으로 지정할 수 있다.
3.1 Establishing the structure of the management operational guidelines
본 연구에서는 로봇의 관리 운영을 위한 키워드를 크게 배치 및 운용과 유지보수 및 관리로 구분 하고 가이드라인의 기본구조를 다음과 같이 제안하였다. 배치 및 운용은 로봇의 기술적 측면의 설정과 사용자 경험에 중점을 두고 이를 사용환경과 사용조건의 범위 내에서 요구되는 조건을 분석하였으며 유지보수 및 관리의 문제는 로봇의 장기적이고 안정적인 운영을 보장하는 측면에서의 조건을 설정하였다. 이 두 체계는 서로 상호 보완 혹은 통합적으로 관리되어야만 공공시설물로서의 역할을 로봇이 효과적으로 수행할 수 있으며 이를 통해 정리된 가이드라인의 구조는 Figure 1과 같다.
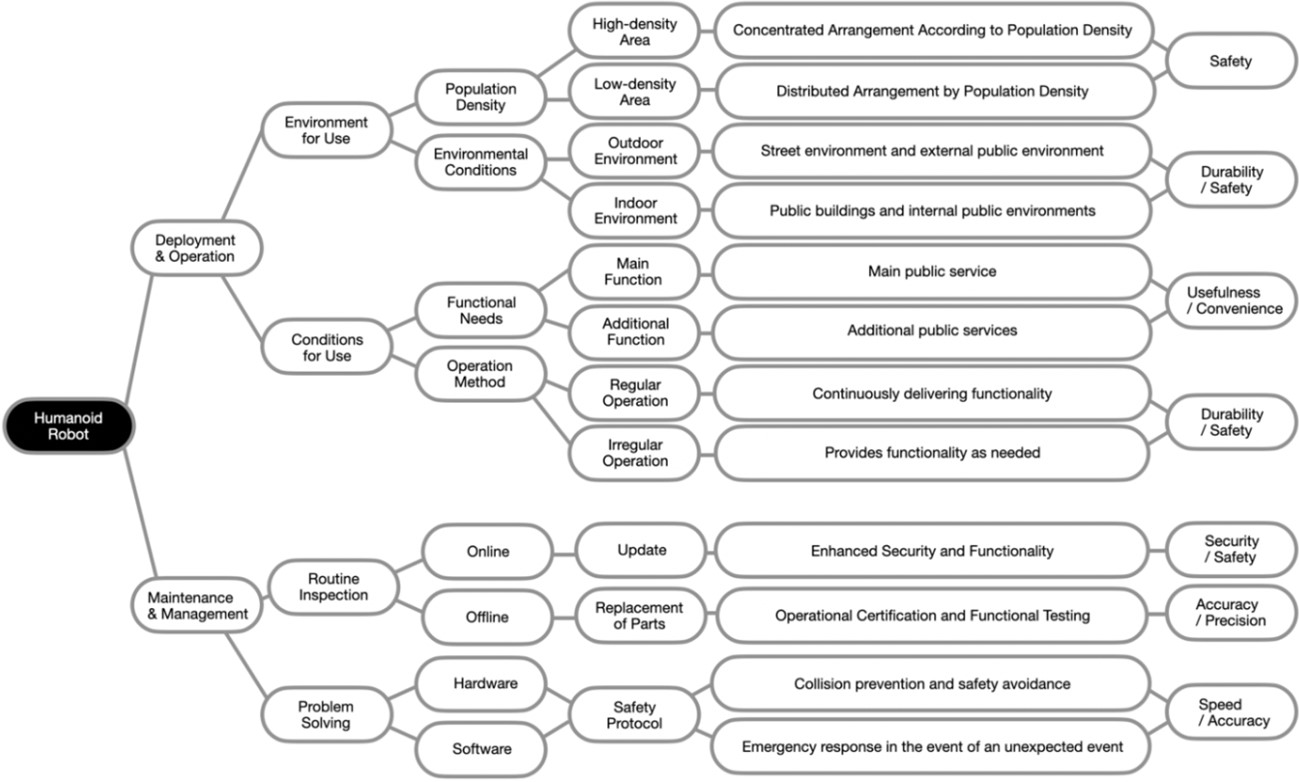
배치 및 운용은 로봇이 실제 어떤 조건의 환경에서 어떻게 사용될지를 결정하는 단계로, 로봇의 효과적인 배치 기준을 통해 공공서비스의 목표를 달성할 수 있는 중요한 요소이다. 이 단계에서는 로봇의 역할 정의, 위치 선정, 기존 인프라와의 통합, 사용자와의 상호작용 방식 등 다양한 부분이 고려되어야 한다. 공공환경에서 배치와 운용이 효과적으로 이루어지지 않으면 로봇의 기능을 최대한 발휘하지 못할 뿐만 아니라, 결과적으로 공공서비스의 질 저하를 초래할 수 있다.
또한 유지보수 및 관리는 로봇이 지속적으로 안전하고 효율적으로 작동할 수 있도록 하기 위한 필수적인 과정이다. 이 단계는 로봇의 하드웨어와 소프트웨어를 포함한 전반적인 상태를 사전에 점검하고, 필요한 경우 수리나 업그레이드를 수행하는 것을 포함한다(Jeong, 2006). 또한, 이 과정에서는 로봇의 보안 문제와 데이터 관리, 법적 사항 등을 고려하여, 장기적으로 안정적인 운영을 보장하는 것이 목적이다. 유지보수와 관리가 적절히 이루어지지 않으면 로봇의 기능성 저하, 고장, 보안유출 등의 심각한 문제가 발생할 수 있어, 공공안전에도 위협이 될 수 있다.
3.2 Establish detailed criteria for management operations guidelines
공공환경에서 기존의 공공시설물을 휴머노이드 로봇으로 대체하여 운용하기 위해서는 각 환경에서 발생할 수 있는 다양한 문제를 사전에 예방하고, 또한 해결을 위한 다양한 기준과 가이드라인이 필요하다. 이는 기존의 시설물에 대한 관리방법과는 다른 개념으로 접근해야 하며 공공환경에서 로봇이 제공하는 공공서비스 기능의 효율적인 활용을 보장하고, 시민의 공공안전과 편의를 극대화하기 위해 로봇의 기능을 효과적으로 제공하고 안전하게 운용될 수 있도록 하는 것이 목표이다. 따라서 본 연구에서는 로봇의 관리 운영을 위한 가이드라인 방향을 Table 2와 같이 다섯 가지 측면에서 고려하였다.
|
Items |
Main
function |
Details |
|
1. User |
User interface |
It should provide an intuitive user
interface so that various users can easily use the robot. |
|
Multilingual translation and
interpretation support |
Information should be provided to
users in various languages so that foreigners can easily use it. |
|
|
Raising awareness |
It is necessary to increase the
positive perception of users through promotional activities on the advantages
and effects of robot |
|
|
2. Safety |
Operational certification |
Regular certification and testing
of operations are required so that robots can operate safely in public. |
|
Collision prevention and |
A system that prevents a robot from
colliding with a person or an |
|
|
Emergency response |
In the event of a robot
malfunction, an emergency response function that can immediately stop
operation is required. |
|
|
User safety training |
Education and promotion programs
should be provided through |
|
|
3. Maintenance |
Regular inspection and |
Regular inspections and maintenance
should be carried out to maintain the performance of the robot and prevent
failures and malfunctions. |
|
Upgrade main function |
Software and hardware updates
should always keep up to date and enhance security. |
|
|
Failure response protocol |
In the event of a robot failure, a
response protocol should be prepared to respond quickly on the spot. |
|
|
4. Privacy |
Data collection and |
The type, purpose, and method of
use of personal information collected by robots should be clarified and user
consent should |
|
Privacy and security |
Personal information is based on
anonymization processing, and appropriate protective measures should be taken
for data security. |
|
|
5. Legal & ethical |
Compliance with the |
It is necessary to ensure that the
operation of the robot complies with |
|
Understanding ethical standards |
Ethical issues or standards
according to the use of robots should |
첫째, 휴머노이드 로봇은 공공환경에서 반복적이고 규칙적인 업무를 효율적으로 수행할 수 있으며, 정보 제공, 시설 안내, 보안 및 검색 등의 기능에서 특히 효율성을 높일 수 있는 장점이 있다(Kim and Kim, 2020). 따라서 접근성 및 사용성 측면에서 다양한 사용자가 로봇에 대한 거부감을 최소화하고 쉽게 사용할 수 있도록 하는 직관적인 사용자 인터페이스(User Interface) 등이 제공되어야 한다.
둘째, 휴머노이드 로봇을 공공환경에 배치하는 경우 안전관리 측면에서 로봇과 사용자 모두의 안전을 보장하는 것이 공공의 신뢰를 유지하기 위해 반드시 필요하다. 특히 공공환경은 많은 사람들이 동시에 이용하는 공간으로 인구 밀집도가 높아 물리적 사고 등도 빈번하게 발생하므로, 이를 사전에 예방하기 위한 안전관리 체계가 필수적으로 수립되어야 한다.
셋째, 휴머노이드 로봇의 지속적인 운영을 위해서는 체계적인 유지보수 계획이 필수적이다. 이는 로봇의 안정적이고 안전한 작동을 보장하기 위해서이며, 단기적으로는 예상치 못한 고장이나 안전사고를 예방하고, 장기적으로는 비용을 절감할 수 있는 특징이 있다. 따라서 이를 위해서는 평소 정기적인 점검과 빠른 문제 해결을 위한 전문 기술 지원 팀의 구성, 실시간 모니터링 시스템의 도입이 필요하다.
넷째, 휴머노이드 로봇은 공공환경에서의 물리적 안전성뿐만 아니라 사이버 보안을 강화하여 정보의 신뢰성을 확보하는 것이 중요하다. 로봇이 수집하거나 처리하는 개인정보 등의 유출이 발생할 경우 개인의 사생활 침해와 같은 문제가 발생할 수 있으며, 이는 공공안전과 공공에 대한 신뢰에도 영향을 미친다. 따라서 이를 위해 정기적인 소프트웨어 업데이트와 보안 점검이 필요하며, 물리적 안전장치와 함께 윤리적 사용 지침을 동시에 마련해야 한다(Jeong, 2006).
다섯째, 휴머노이드 로봇 도입과 운영을 지원하는 정책적, 법적 규제를 적극적으로 개선해야 한다. 이는 로봇이 불법적이거나 규제위반의 위험을 방지하고, 윤리적으로 공정하고 차별없이 사용자를 대하며, 인간의 존엄성과 권리를 존중하도록 보장한다. 따라서 가이드라인 체계 구축을 통해 공공의 신뢰를 유지하고 사회적 수용성을 높이는데 있어 안정적인 로봇 운영을 사전에 보장할 수 있다.
3.3 Survey and expert verification
본 연구에서는 먼저 휴머노이드 로봇의 관리 운영을 위한 가이드라인 구조 체계와 세부 기준을 도출한 후, 이를 검증하기 위해 전문가 대상 설문조사를 진행하였다. 설문조사는 2024년 9월 1일부터 9월 10일까지 공공디자인 관련 실무 경험이 있고 관련 용역 및 연구 경험이 있는 공공디자인 분야의 전문가 8명을 대상으로 진행되었으며, 조사의 개요는 Table 3과 같다.
|
|
Delphi method interview |
|
Period |
September 1, 2024 to September 10, 2024 |
|
Survey object |
A total of 8 experts in public design (10 years or more of
experience) (2 Public design researchers, 6 Professors) |
|
Purpose |
Get expert feedback on guideline content
via email after pre-interview |
본 연구의 이해를 위해 평가에 앞서 먼저 전문가들에게 이 연구의 배경, 목적 등을 숙지할 수 있도록 자료를 제공하고 사전 인터뷰를 통해 본 연구의 이해도를 높였으며, 설문 문항은 연구방향의 타당성, 가이드라인 구조 및 체계의 명확성, 가이드라인의 세부 항목별 내용의 타당성, 가이드라인 항목별 의미의 명확성, 기타 의견 등 5가지 항목으로 구성되었고, 이후 최종 의견을 이메일로 전달하는 방식으로 진행하였다. 설문조사 과정에서 사용했던 평가 지표와 질문내용은 Table 4와 같다.
|
Evaluation indicators |
Question content |
|
Validity of research topics |
In this study, we newly established the concept of humanoid robots
as public facilities |
|
Clarity of humanoid robot management and operation guidelines structural
system |
In this study, a structural diagram was developed for the
management and operation of humanoid robots in a public environment. Please
give us your opinion on whether you can understand this structural diagram
clearly. |
|
Validity of humanoid robot management and operational guidelines
by detailed item |
In this study, we derived guidelines for the management and
operation of humanoid robots as public facilities in public environments.
Please give us your opinion on |
|
Itemized clarity of meaning in |
Please give us your opinion on whether the meaning of each
Detailed Item is clear |
|
Additional comments from |
Please give us your opinion if there is anything to add to the
humanoid robot management and operation guidelines you have evaluated so far. |
4.1 Expert response results
설문결과, 응답자는 대부분 사전에 예측이 가능한 유지보수의 중요성을 강조했으며, 또한 데이터 보안 체계의 단계별 강화가 필요하다고 응답하였다. 또한, 로봇의 주기적 점검과 각 단계별 긴급 대응 방안의 구체적인 필요성을 언급하였으며, 이러한 피드백은 가이드라인의 방향 및 세부구성에서 몇 가지 중요한 수정이 이루어졌다. 관리 측면에서 유지보수에 대한 새로운 방법이 기존의 정기적 점검 체계에 추가로 고려되어, 실시간으로 로봇의 상태를 실시간으로 모니터링하고 문제를 사전에 감지할 수 있는 시스템에 대한 방법을 포함했으며, 보안 측면에서는 로봇의 데이터 수집 및 전송 과정에서의 보안 프로토콜을 강화하는 부분이 수정, 보완되었고, 개인정보 보호와 관련된 구체적인 지침과 법 규제와의 연동을 추가로 고려하였다. 각 전문가들의 의견을 정리하면 Table 5와 같다.
|
Evaluation
indicators |
Contents of response |
|
Opinion 1: |
1.
I think the direction and guideline scenario for the concept is appropriate
and valid 2.
It is necessary to clarify whether the direction of the study is the management
of public facilities or humanoid robots. 3.
The subject and direction of this study is very valid as a practical,
realistic, and differentiated approach 4.
The development of public design and the combination of humanoid robots make
sense in the direction of research. 5.
I think the proposal of the management plan and guidelines for public
facilities using robots is a necessary study at this point 6. The subject matter and the direction of
the study are considered very reasonable 7. It is considered reasonable as a study
to secure expandability for robots |
|
Opinion 2: |
1. The structural diagram clearly and
intuitively expresses complex content. 2. It is recommended that the specific
role of the robot be included in the guidelines. 3. The structure of the guidelines is
systematic, clear, and well-understood. 4.
There is no problem in understanding the concept of management and operation
in the guideline structure. 5.
The structure of the guidelines is clear, but it is also necessary to
separate the concepts step by step. 6. Rules and elements for the management
of humanoid robots are appropriate. 7.
I think the structural diagram is a little complicated and some additional
explanations of classification criteria are needed. 8.
The structure is generally clear, but more content needs to be supplemented
for understanding. |
|
Opinion 3: |
1. Guidelines for the management of robots
outside of operating hours also seem necessary 2. I think we need additional logic on
maintenance in detail. 3. The details of this guideline are valid
as they maintain essential standards. 4.
There is no problem with the detailed items, but some specific examples are
required for each item 5. The details of the guidelines are
reasonable and well understood 6. The details of the guidelines are very
well listed and appropriate 7. It is necessary to adjust some of the
order for the classification of guideline details 8. Most of the details are valid, but some
words need to be modified. |
|
Opinion 4: |
1. The meaning of each item in the
guidelines is judged to be clear. 2. Need to separate humanoid robot
management by purpose and function. 3. The humanoid robot management and
operation guidelines are specific and clear. 4. The meaning of each item is fully
understood and some items require examples. 5.
Overall, the meaning is clear, but I think the terminology needs to be
reviewed in safety management. 6.
The items in the guidelines are clear, but it would be good to consider
adding the steps of the detailed items. 7. After some modification of the
guideline classification, the contents must be rearranged. |
|
Opinion 5: |
1. It is suggested that a review of
scenarios for various environments is needed. 2.
I believe that it is also good to consider the concept of environmental
adaptability in the management details of the humanoid robot 3.
The step-by-step development prediction of robots used in public environments
and the addition 4.
I think it is also desirable to add information about user accessibility or
usability or user experience 5. An approach to integrating operational
manuals and guidelines is also required 6. It also proposes to add content about
national and international standards |
4.2 Step-by-step implementation of management operation guidelines
최종적으로 도출된 단계별 세부 추진 방안은 휴머노이드 로봇의 관리 운영을 체계적으로 실행하기 위한 구체적인 절차를 포함한다. 각 단계는 로봇의 초기 설치부터 일상 운영, 유지보수, 보안 관리에 이르기까지 모든 운영 과정에서 요구되는 필수적인 요소들을 포함하고 있다.
로봇의 기술은 급속하게 발전하고 있지만 공공환경에 배치하는 초기의 도입단계에서는 성능 및 안전성에서 신뢰성을 검증해야 한다. 또한 휴머노이드 로봇이 공공시설물로 도입될 경우 사용자인 일반 시민들의 거부감 없는 사회적 수용 또한 매우 중요한 요소이다(Koh and Nah, 2023). 이는 단계별 도입을 통해 익숙해지는 시간을 제공해야 한다. 그리고 로봇의 초기 대량 도입은 경제적 부담을 가중시키므로 소규모로 운영 후 성과를 평가하는 단계를 거쳐야 하며 휴머노이드 로봇을 공공시설물로 원활하게 활용하려면 데이터 통신망, 충전 시설, 등의 기반 인프라도 사전에 잘 갖춰져 있어야 한다.
따라서 도시 공공시설물로서 휴머노이드 로봇을 관리하기 위해 단계별로 세부 추진 방안을 마련하는 것은, 로봇의 효율적이고 안전한 운영을 보장하기 위해서 필수적인 부분이다. 각 단계에서의 명확한 계획과 실행은 로봇이 공공서비스를 제공하는 과정에서 발생할 수 있는 다양한 문제를 사전에 예방하고, 문제 발생시 신속하게 대응할 수 있도록 돕는다. 또한 체계적인 관리 방안은 로봇의 성능을 지속적으로 최적화하고, 사용자의 신뢰를 유지하며, 공공시설물로서 로봇의 장기적인 운영과 안정성을 보장하는데 중요한 역할을 한다. 따라서 본 연구의 로봇의 관리와 운용을 위한 가이드라인의 단계별 세부 추진 방안은 다음의 5가지의 단계로 구분하였으며 세부내용은 Table 6과 같다.
|
Step-by-step
standard |
Details |
|
|
Step 1 |
Setting goals |
It clearly defines the purpose and
role of the robot's introduction, and sets specific functions and tasks to be
performed by the robot. |
|
Environmental analysis |
It analyzes the characteristics and
conditions of the public environment in which the robot will be deployed, and
considers the physical characteristics of the space and user accessibility. |
|
|
Design and integration |
We plan how the robot will be
integrated with the existing infrastructure of the city, and consider
interaction and integration |
|
|
Step 2 |
Test deployment |
Before deploying the robot in each
environment, test operations are used to identify unexpected problems or
environmental factors. |
|
Initial deployment |
Based on the test results, the
location of the robot in each environment, the movement line, and the way it
interacts with the |
|
|
User training and |
It informs users of how to use the
robot and safety guidelines, and conducts promotions to help them understand
the role of the robot. |
|
|
Step 3 Operational and |
Real-time monitoring |
The robot's condition and
performance are monitored in real time to detect and respond to anomalies
early. |
|
Update |
It continuously updates the robot's
software to add new features or improve existing ones. |
|
|
Troubleshooting |
Prepare a support system that
allows robots to respond quickly to problems that arise during operation. |
|
|
Step 4 Maintenance and |
Regular inspection |
Check the robot's hardware and
software regularly and perform repairs or parts replacement if necessary. |
|
Security management |
Maintain the robot's data and
network security and prepare for cyber threats such as hacking and data
leakage. |
|
|
Compliance with |
Manage robot operations to comply
with relevant laws and regulations, and adjust operational policies to legal
standards if necessary. |
|
|
Step 5 Evaluation and |
Performance evaluation |
The operation performance of the
robot is regularly evaluated to check whether the goal is achieved, and
necessary improvements are derived. |
|
Collect user feedback |
By collecting feedback on the
experiences of citizens who interacted with robots, we seek ways to improve
the user experience. |
|
|
Improvement and expansion plans |
Based on the evaluation and
results, the operation of the robot is improved, and more robots are deployed
as needed or new features are introduced. |
|
본 연구는 가이드라인의 구조를 설정, 세부 기준 도출, 타당성 검증이라는 세 가지 단계로 구성된 체계적인 접근을 취하고 있다. 이는 특정환경을 전제로 로봇 운영 가이드라인을 설정하는 기존 연구와 일부 유사하지만 단계별로 명확히 구분된 접근을 강조한다는 점에서 차별화 된다.
향후 도시에는 다양한 기술이 통합적으로 활용될 것으로 예상된다. 따라서 본 연구를 통해 휴머노이드 로봇을 도시 인프라에 포함시켜 도시 운영의 효율성을 높이는데 기여할 수 있으며 가이드라인을 통해 다양한 공공서비스의 질의 향상을 기대할 수 있다. 또한 연구에서 제시된 가이드라인 기준은 로봇 제조사나 서비스 제공자가 시스템을 구축하거나 운영하는 과정에서 중요한 자료로 활용될 수 있다.
그러나 본 연구에서 제시된 가이드라인은 실제 현장에 적용되지 않아 그 효과성을 실질적으로 검증할 기회가 부족하며 실제로 적용되는 과정에서 예상 가능한 결과에 대해 추가적인 실증연구가 필요하다. 특히 연구에서는 현재의 기술과 환경수준에 근거하여 가이드라인을 제시했지만 향후 지속적으로 변화하는 기술과 환경에 따라 추가적으로 발생할 수 있는 불확실성 요소에 대해 지속적인 업데이트가 요구된다.
본 연구에서는 도시 공공시설물로서 휴머노이드 로봇의 효과적인 관리 및 운영 방안을 체계적으로 정립하기 위해 다음과 같은 세 가지 단계별 연구 방향을 설정하여 연구를 진행하였다.
첫째, 휴머노이드 로봇의 효율적인 운영과 관리를 위한 가이드라인의 기본적인 체계를 설정하였다. 이 가이드라인 체계는 로봇의 배치 및 운용, 관리 및 유지보수 차원에서 다양한 요소를 종합적으로 고려하여 구성되었으며 이를 통해 로봇이 공공서비스 제공에서 원활하게 기능할 수 있는 전반적인 관리 체계의 기본 틀을 마련하는데 중점을 두었다.
둘째, 설정된 가이드라인을 구체화하여 항목별 세부 기준을 도출하였다. 세부 기준은 로봇을 운영하는 각 단계에서 적용할 수 있는 실질적인 운용 기준과 구체적인 관리 방침 및 절차를 포함하며, 로봇의 관리 및 유지보수를 보다 체계적으로 실행할 수 있는 지침을 도출하였다. 이를 통해 로봇의 안정적이고 효율적인 운용을 보장할 수 있도록 하였다.
셋째, 가이드라인의 체계와 세부내용에 대해 전문가 조사를 실시하여 그 타당성을 검증하였다. 검증 결과를 반영하여 가이드라인 내용을 개선하고, 이를 근거로 가이드라인을 단계별로 세분화하여 구체적인 추진 방안을 제시하였다. 이를 통해 로봇 운영의 각 단계를 시스템화 하여 일관되게 관리될 수 있도록 하였으며, 로봇의 공공환경의 통합을 전제로 체계적인 운영이 가능하도록 하였다.
결론적으로, 본 연구에서 제시된 가이드라인은 휴머노이드 로봇의 공공시설물로서의 도입과 운영을 위한 중요한 기틀을 마련하며, 공공서비스의 질적 향상과 효율적인 관리 체계를 구축하는 데 유효한 도구를 제시했다는 점에서 중요한 의의를 가진다. 향후 연구에서는 제안된 가이드라인을 실제 운영 현장에 적용하고, 이를 기반으로 한 추가적인 실증 연구를 통해 관리 및 운영의 효과성을 검증할 필요가 있다. 이를 위해 품질 관리 및 효율성과 프로세스 관리를 위한 P(Plan)-D(Do)-C(Check)-A(Act) 사이클 프로세스를 관리도구 차원에서 추가로 검토하여, 지속적으로 변화하는 기술과 환경이 반영된 가이드라인의 지속적이며 체계적인 문제해결을 목표로 단계별 순환 과정과 지속적인 업데이트에 대해 추가적인 연구가 필요할 것으로 보인다.
References
1. Choi, M.J., Dong, J.U. and Lee, H.R., The Efficient Management of Public Facilities in Local Governments - - Focusing on the policies of Korea and Japan - Journal of the Korean Institute of Educational Facilities, 3-12, 2020, doi:10.7859/kief:2020.27.6.001.
Google Scholar
2. Chung, S.E., User Expectation Experience by Service Type of Social Robot, Journal of Integrated Design Research, 19(1), 9-25, 2020, doi:10.21195/JIDR.2020.19.1.001.
3. Design Gyeonggi., Gyeonggi-Do Public Design Guideline, Design Gyeonggi, 2010, http://design.gg.go.kr (retrieved February 20, 2010).
4. Design Gyeonggi., Gyeonggi-Do Public Design Master Plan, Design Gyeonggi, 2010, http://design.gg.go.kr (retrieved February 20, 2010).
5. Design Gyeonggi., Gyeonggi-Do Public Design Guideline revised edition, Design Gyeonggi, 2020, http://design.gg.go.kr (retrieved March 10, 2020).
6. Design Gyeonggi., Gyeonggi-do Public Design Promotional Plan, Design Gyeonggi, 2020, http://design.gg.go.kr (retrieved March 10, 2020).
7. Jeong, J.K., Legal System and Interpretation for Network Robot Services. Kangwon law review, 23, 131-169, 2006.
8. Kim, T.K. and Pan, Y.H., A Study on Humanoid Robot Trends and Development Standards by Type: Based on Leisure and Entertainment Area, Korea Service Design Council, 2024(1), 91-96, 2024.
9. Kim, B.S. and Kim, S.I., User Preference for the Personification of Public Service Robot, Journal of Digital Convergence, 361-366, 2020, doi:10.14400/JDC.2020.18.2.361.
Google Scholar
10. Koh, H.J. and Nah, K., A Case study of Service Robot Interaction Design according to Purpose of Use: focusing on Feedback, Design Research, 321-332, 2023, doi:10.46248/kidrs.2023.1.321.
Google Scholar
11. Park, J.H., Lee, Y.S and Park, B.M., A Study on Basic Items For Public Facility Design Evaluation - Focused on Public Facility Design in Busan -, Archives of Design Research, 351-360, 2011.
12. Shin, D.W., Baek, S.M., Lee, J.W. and Lee, S.H., Development of HRI integration technology to improve dependability for Home/ Public Service Robot. The Korean Instituteof Broadcastand Media Engineers, 7-11, 2008.
Google Scholar
13. Zhang, Y.H., Study on Seoul City Public Accommodation Thing Policy and Design Directionality, Journal of Integrated Design Research, 11(1), 133-147, 2012, doi:10.21195/JIDR.2012.11.1.010.
PIDS App ServiceClick here!